Weekly Tech Recap - № 202 - Raspberry Pi boutique, Password Checkup, KeySteal, new emojis, etc.
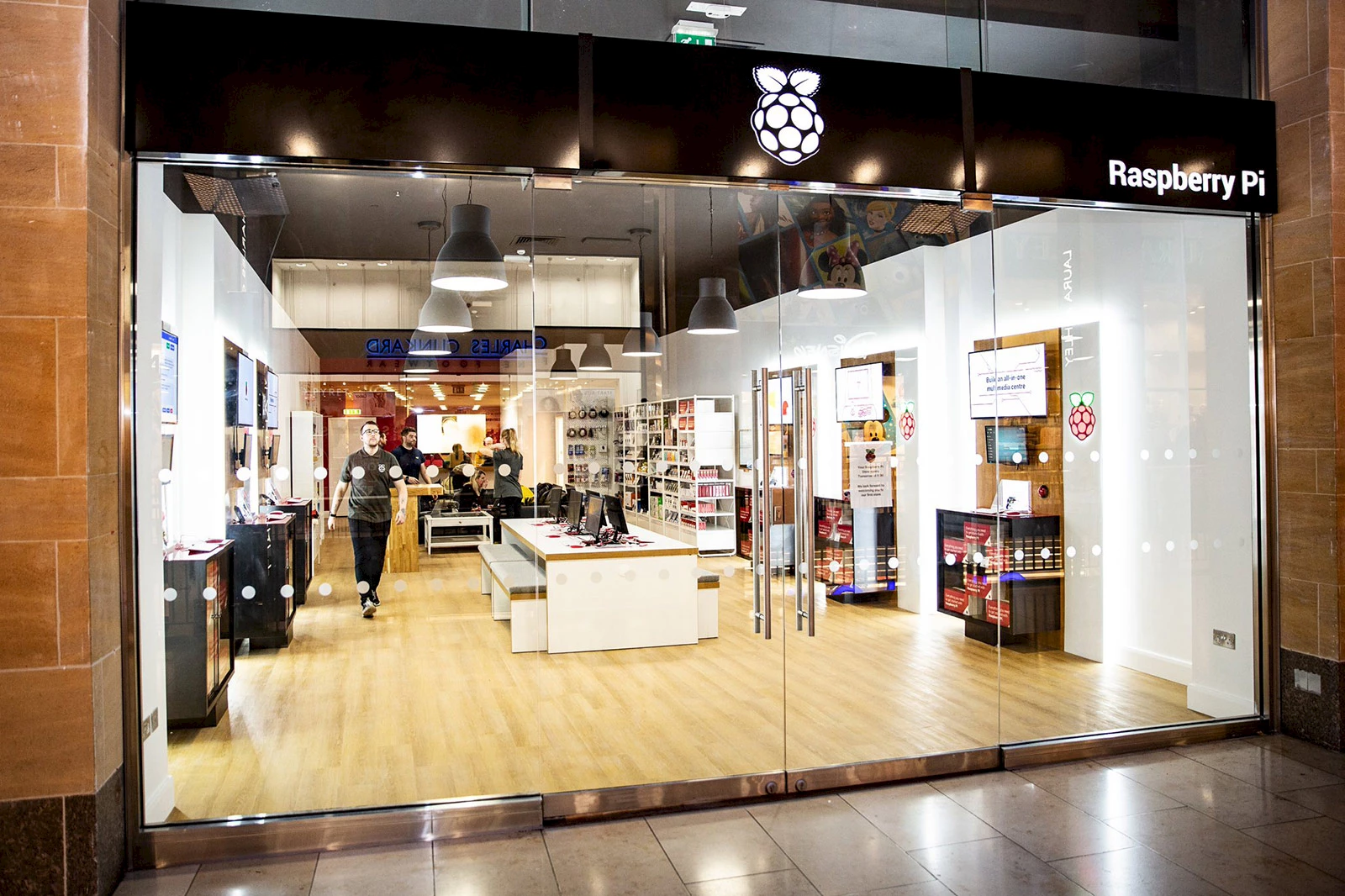

Raspberry Pi boutique
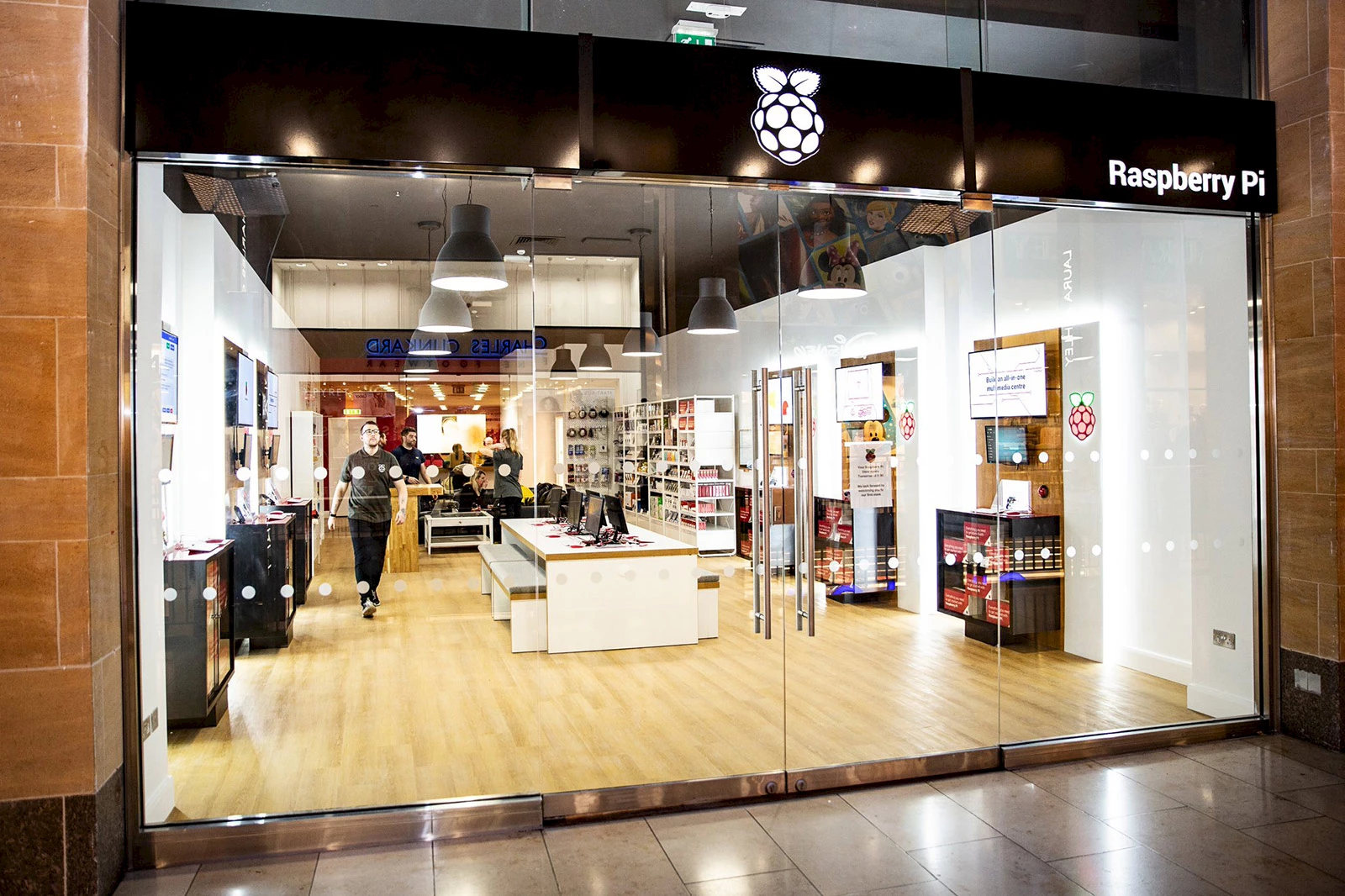
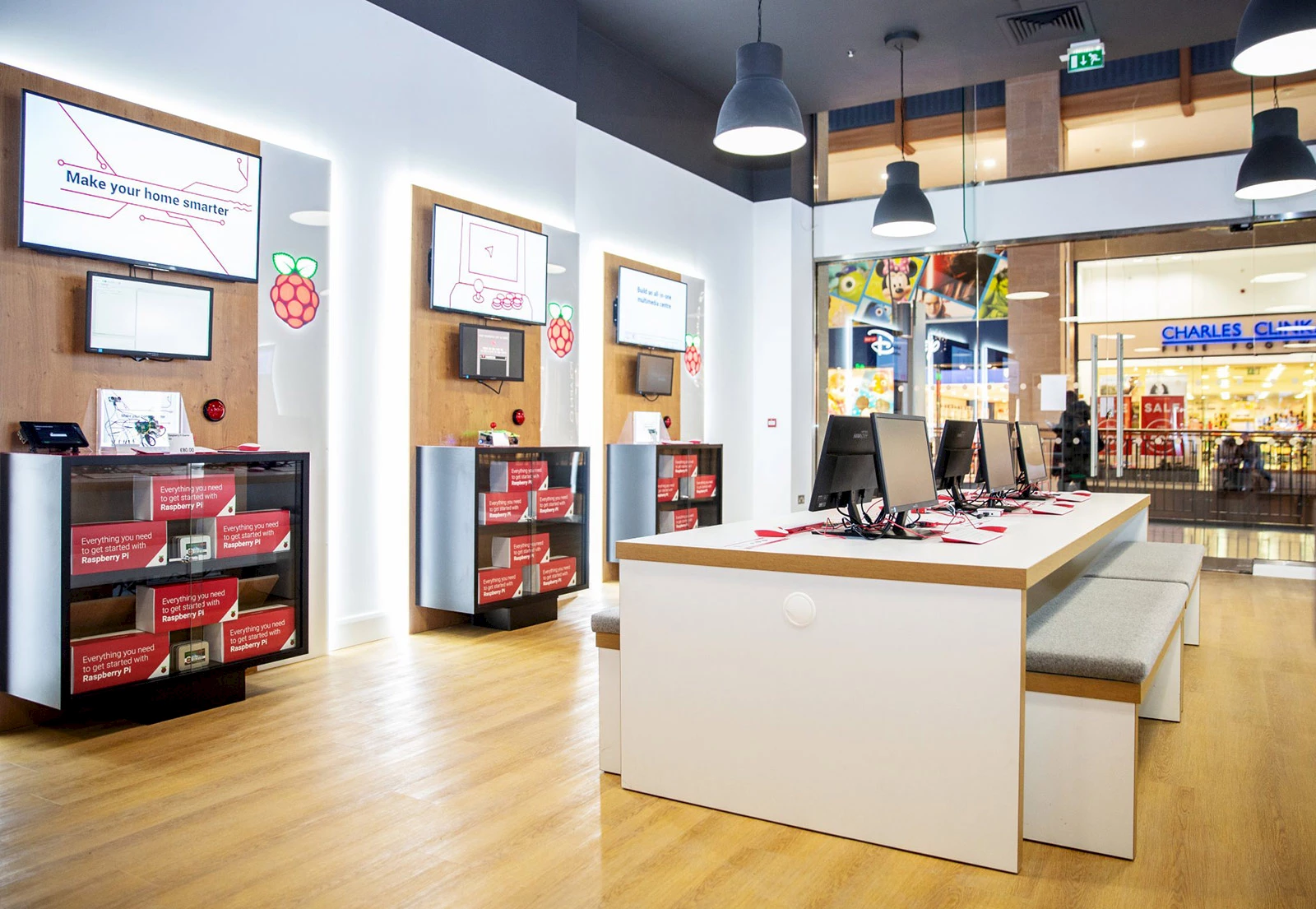


Raspberry Pi Store. © Raspberry Pi Foundation.
The Raspberry Pi Foundation opened a boutique in the Grand Arcade shopping center in the heart of Cambridge, home of the world’s most famous nano-computer. You can buy the Raspberry Pi, of course, but also additional modules, accessories, books, magazines, objects and gadgets bearing the raspberry logo. Much like an Apple Store, the store also has a pedagogical mission and helps newbies get acquainted with technology, try out programming and see examples of what can be done with this very accessible computer.
Concurrently, the foundation announced a new starter kit for beginners. It includes the latest Pi 3 Model B + as well as a keyboard, a mouse, an SD card, a power supply, an HDMI cable and a book explaining the basics of Pi. In short, all you need is a screen to start. Costing GBP 80 (CAD 138), it will initially only be sold in the Cambridge bricks-and-mortar store, but it will soon also be available online. Established six years ago, the Raspberry Pi Foundation has sold 19 million of its low-cost single-card PCs.
⇨ TechCrunch, “The Raspberry Pi store is much cooler than an Apple Store.”
Password Checkup

© iStock.
Google has released a Chrome extension called Password Checkup. Its role is to check passwords, both those stored in the password manager and those you enter manually, to ensure that they are not associated with hacked accounts. It operates through a Google database that stores data from more than 4 billion compromised accounts, allowing it to detect whether the identifiers you use are in this database. If so, it alerts you. If you’re not comfortable with your account credentials going through a third party, Google wants to reassure you: Password Checkup uses a combination of anonymization and cryptography to protect the exchange, with a technique called “blinding,” which creates a secret search index. The identifiers are anonymized with an Argon2 hash function to create a search key, and encrypted through elliptic-curve cryptography.
⇨ Chrome Web Store, “Password Checkup.”
⇨ Ars Technica, “Google releases Chrome extension that alerts users of breached passwords.”
macOS Keychain Access failure
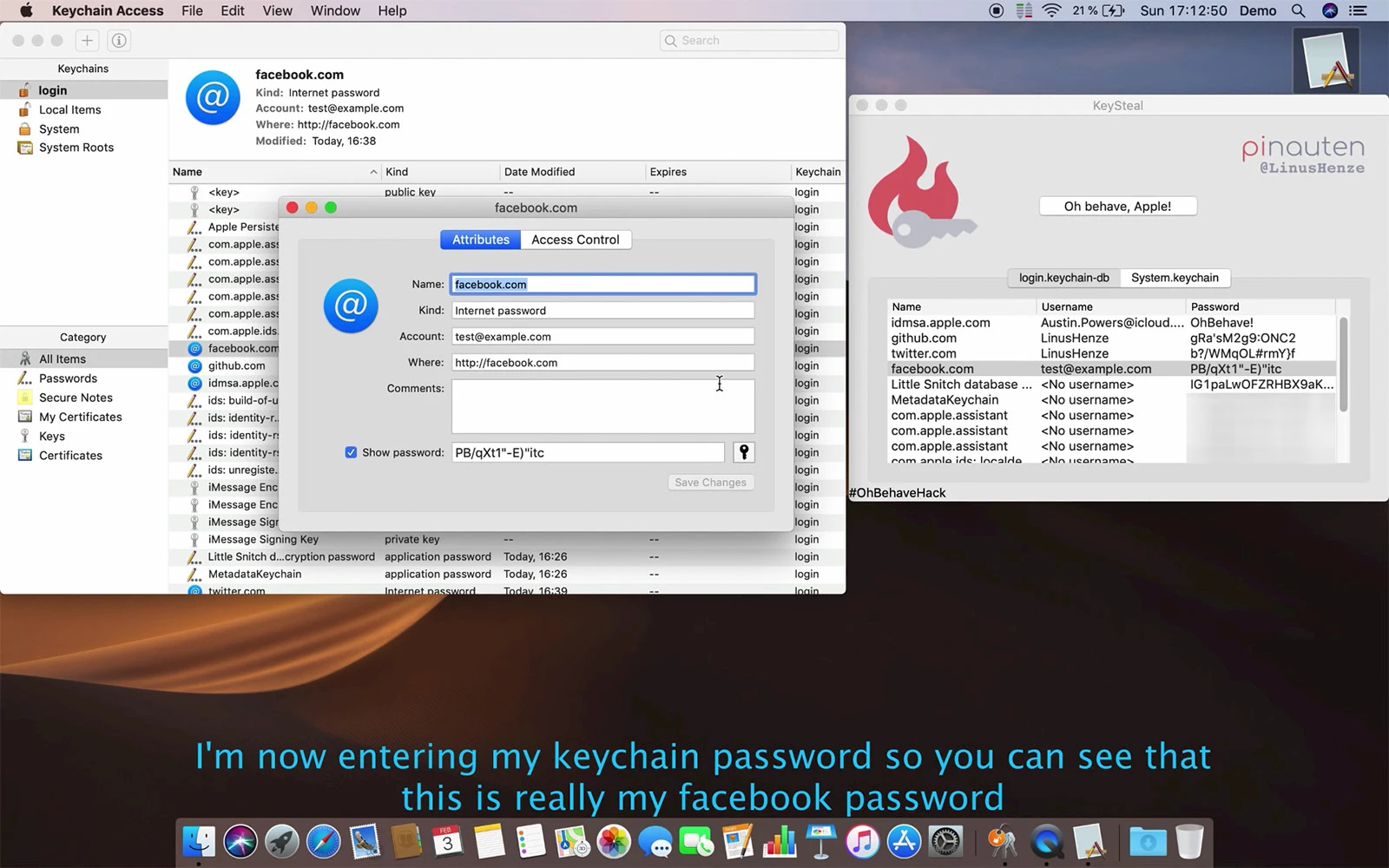
KeySteal. © Linus Henze.
Cybersecurity specialist Linuz Henze has discovered a major security breach in the Keychain Access application on macOS Mojave, which is specifically responsible for protecting all your login credentials and sensitive information (passwords, certificates, secure notes, etc.). This flaw allows access to all passwords without requiring an administrator password, which is alarming. In addition, the expert explains that he has no intention of revealing the details of the flaw to Apple, as a means of expressing his displeasure that there is no “bug bounty” — a reward program for those who discover a vulnerability — for macOS, while one exists for iOS. He also encourages other researchers to publicize the security issues they discover in order to put pressure on Apple to offer a suitable bug bounty for macOS. “Finding vulnerabilities like this one takes time, and I just think that paying researchers is the right thing to do because we’re helping Apple to make their product more secure,” he contends.
⇨ Cult of Mac, “macOS Mojave flaw puts your Keychain passwords at risk.”
Google pulls 29 photo apps from Play Store

© iStock.
According to the security company Trend Micro, Google has removed 29 malicious Android applications from its Google Play Store. These are applications that in appearance improve and transform photos, but in fact hide malicious features. Of the 29 applications, 11 were downloaded more than 100,000 times, and three of them were downloaded more than 1,000,000 times. The three apps with the greatest number of downloads that were suppressed are Pro Camera Beauty, Cartoon Art Photo, and Emoji Camera. Other deleted apps include Art Editor, Super Camera, Art Effects for Photo, Art Effect, Prizma Photo Effect, and Pixture. Protecting its store and its users from potentially harmful apps seems like a challenge for Google. The moral is, be cautious when you download an app that does not come from a known publisher. Check other users’ comments. If critics mention suspicious behavior, it may be wise to refrain from downloading the application.
⇨ Trend Micro, Security Intelligence Blog, “Various Google Play ‘beauty camera’ apps send users pornographic content, redirect them to phishing websites and collect their pictures.”
⇨ Engadget, “Google pulls 29 photo apps that stole pictures and promoted scam.”
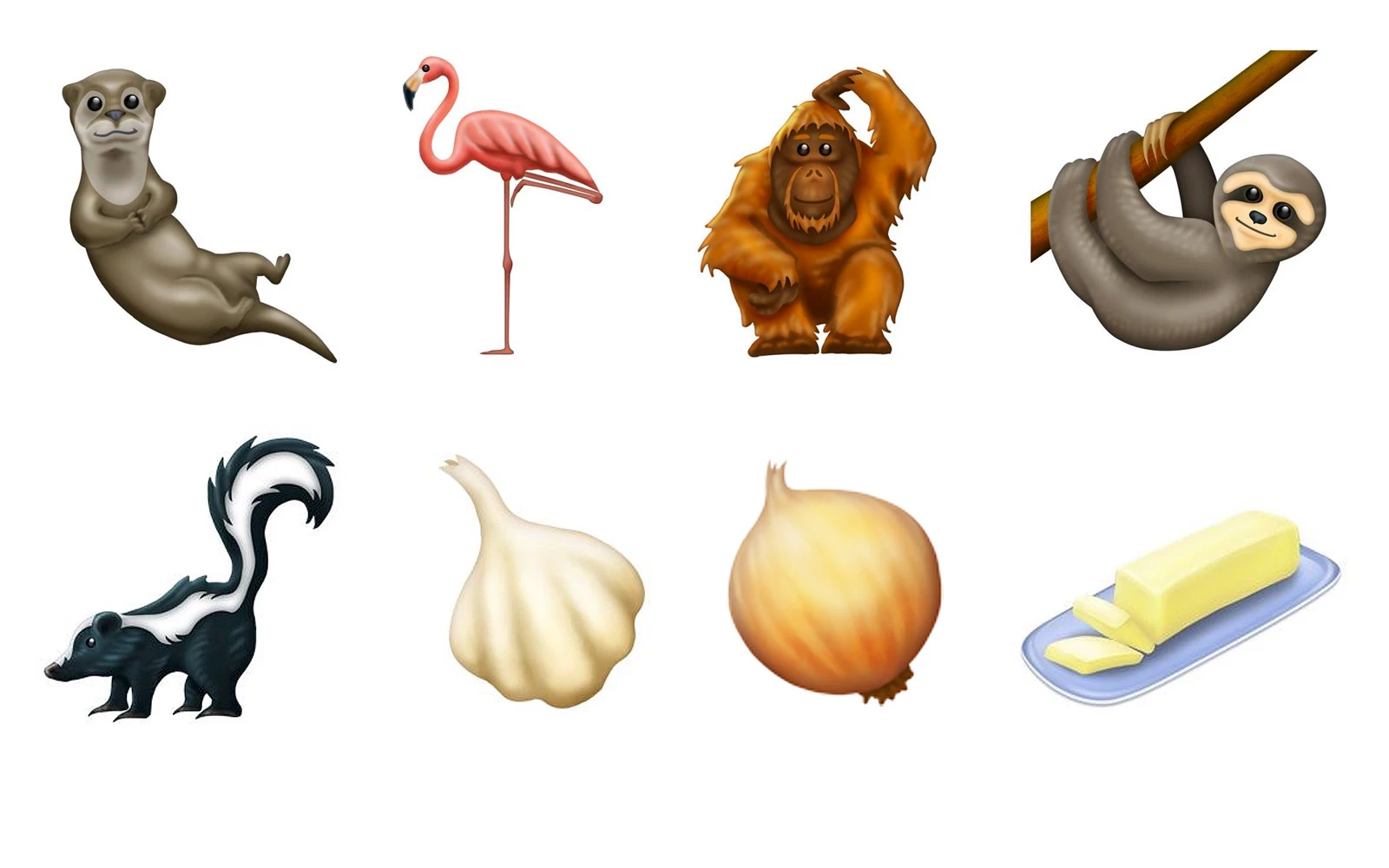
230 new emojis

© Emojipedia.
Unicode finalized a list of 230 new emojis for 2019. That might sound like a lot, but if we don’t count the new variations of colors, skin tones and gender, it’s actually only 59. But these are really essential emojis! How have we gotten this far without a cute otter, an endearing sloth, a sly skunk, a goofy orangutan or a graceful flamingo? And our recipes have not been the same since the appearance of the indispensable garlic, onion and butter. You can even sit on a chair and play banjo. In addition, the consortium has added a series of emojis pertaining to disabilities: there are two guide dogs, motorized or unmotorized wheelchairs, prosthetic arms and legs, ears with hearing aids, figures that sign that they are hard of hearing, a white cane for the blind, and figures using this cane to guide them. Most users will see these new emoji upload to their devices throughout 2019 with software updates.
⇨ Emojipedia, “230 new emojis in final list for 2019.”
